Transformer Testing Course – e-lesson #18: Testing of tap-changers and built-in current transformers

Hosted by:
Lesson 18 of the Transformer Testing series focuses on the testing of critical components such as tap-changers (OLTC, DETC) and current transformers (CT), which are integral to the operation of power transformers. These components undergo routine testing by their manufacturers, but testing is also necessary after they are integrated into the transformer. This lesson covers the procedures for testing these components during the FAT (Factory Acceptance Testing) of transformers.
Key Topics Covered in the Lesson:
1. Tap-Changers Overview:
- Tap-changers are devices used to regulate the voltage of a transformer by varying the turns ratio. There are two main types: on-load tap-changers (OLTC) and off-circuit tap-changers (DETC, OCTC). OLTCs allow voltage adjustments while the transformer is energized, without interrupting the supply, while OCTCs operate when the transformer is de-energized.
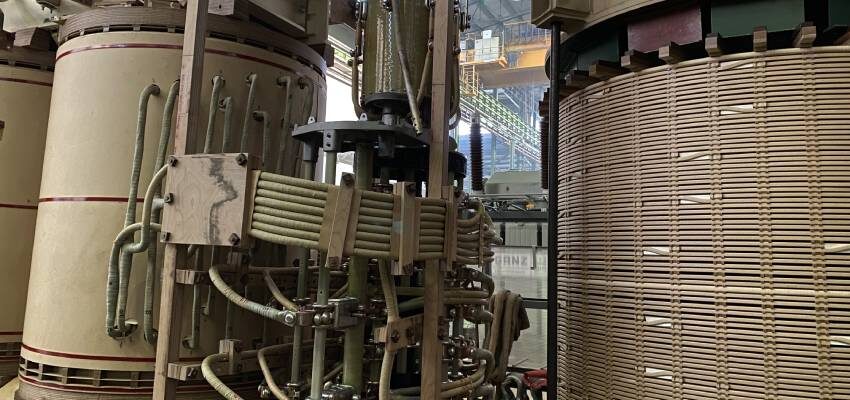
2. On-Load Tap-Changer (OLTC) Construction and Functionality:
- The OLTC consists of several key components: the tap selector, the diverter switch, and the change-over selector. These components work together to select different tap positions and manage the load currents and step voltages.
- The OLTC is tested for its operation at various stages, including with the transformer de-energized, at reduced auxiliary voltage, and under energized conditions. The test ensures the correct operation of the tap-changer and checks for mechanical and electrical end positions.
3. Testing Procedures for OLTC:
- The OLTC is subjected to multiple tests, including:
- Operation tests with the transformer de-energized (8 complete cycles)
- Operation tests with reduced auxiliary voltage to ensure sufficient torque
- Tests with the transformer energized at no load
- Tests under load, with the transformer energized at rated current
4. Off-Circuit Tap-Changer (OCTC):
- OCTCs are designed for use when the transformer is de-energized and are manually or motor-driven devices that select different taps to vary the turns ratio. The lesson explains how these devices function and how to test them to ensure proper contact and prevent overheating.
5. Testing of Built-In Current Transformers (CT):
- Current transformers built into the transformer are tested for correct assembly and connection. Common issues include reverse polarity, incorrect wiring, and insulation problems.
- Various tests are conducted to check the ratio, polarity, and insulation of the CTs. These include:
- Ratio and polarity tests using voltage ratio meters and primary current injection methods
- Insulation tests of the secondary circuit of the CTs to ensure they meet the required standards for voltage withstand.
6. Standards for Testing:
- The lesson references key standards related to transformer and tap-changer testing, including IEC 60076, IEC 60214, IEC 61869-2, and IEEE Std. C57.12.90, among others. These standards guide the testing procedures to ensure that the components meet the required performance and safety criteria.
Why These Tests Matter:
The importance of testing tap-changers and current transformers during the FAT process cannot be overstated. These components play a critical role in ensuring the reliability and efficiency of power transformers. Proper operation of the OLTC ensures that voltage levels are adjusted accurately during operation, while CTs are essential for measuring current and monitoring transformer performance. Any malfunction or improper assembly can lead to operational inefficiencies, transformer failures, or safety risks.
Unauthorized message
The author will explain the tap-changers and built-in current transformers, as important components of the power transformer. After the live session, the e-lesson stays available on demand.
About the author
Balazs Sztari
Ganz ElectricBalazs Sztari graduated as electrical engineer in Budapest. Beside of factory acceptance tests, his team performs commissioning, diagnostics and R&D tests on power transformers and rotating machines.
He is currently a member of Cigre A2.53 working group.